The field of industrial robotics has been recently undergoing a transformative evolution, as new technologies (e.g., Artificial Intelligence (AI) and cloud computing) and novel business models (e.g., robot-as-a-service (RaaS)) are reshaping the landscape and gradually pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Therefore, modern industrial organizations have better understand the most recent industrial robotics trends and robotics industry developments, which entail the interplay between humans and robots, as well as the integration of advanced technologies into robots.
Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC)
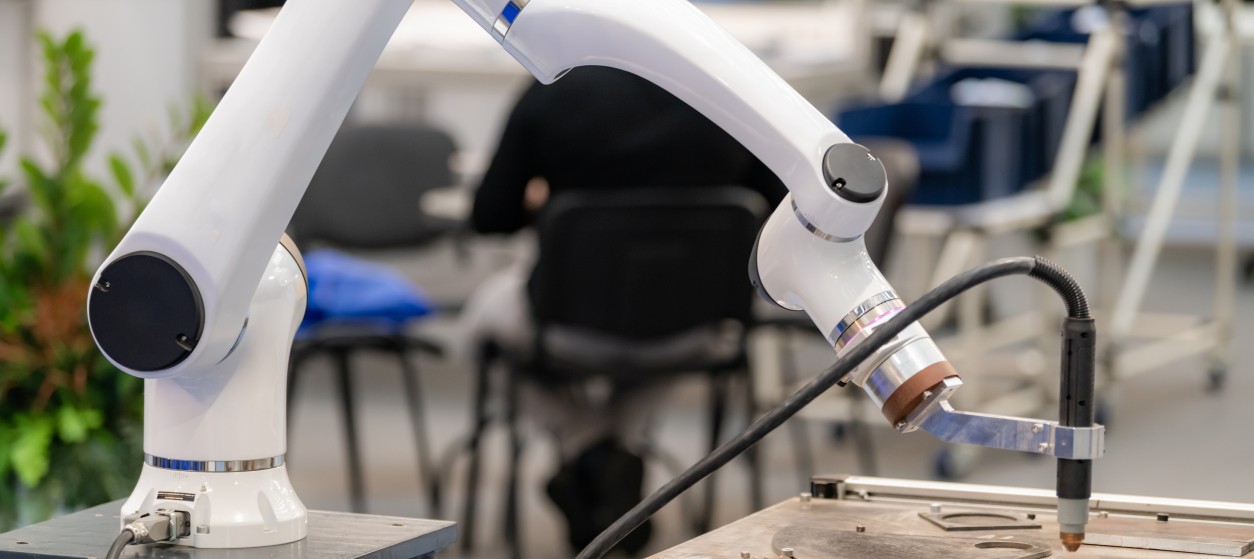
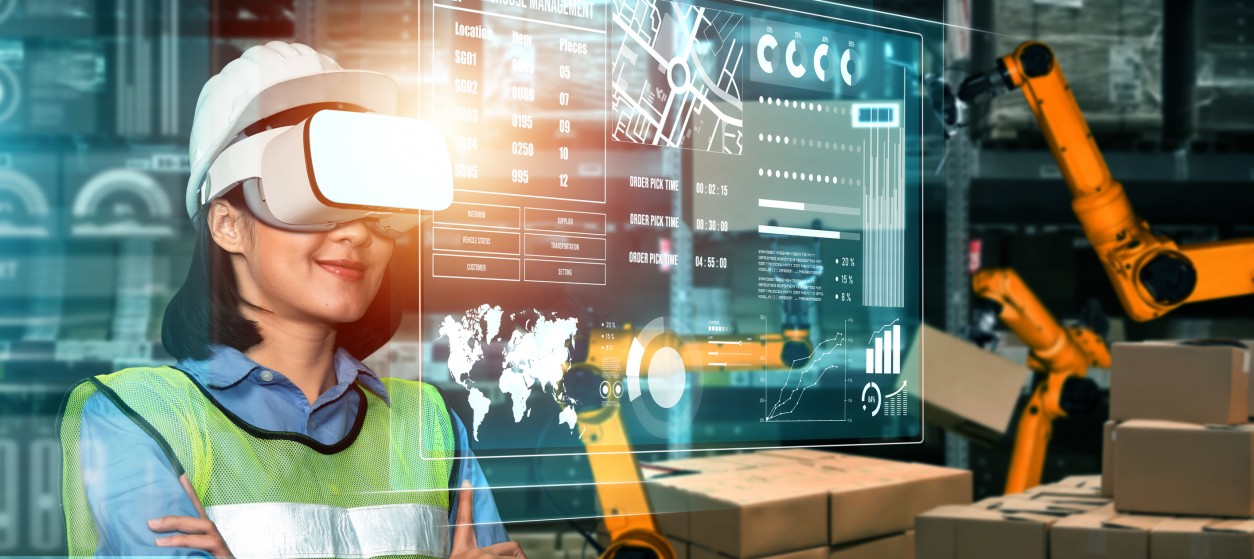
During the last couple of years, there has been an ongoing transition from conventional digital manufacturing and cyber-physical production systems (i.e., Industry 4.0 and Industry 4.0 Robotics) to human-centered manufacturing systems (Industry 5.0). This transition is very much driven by the emergence and rise of Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC). Traditionally, robots were isolated within “safety cages”, which were destined to limit their interactions with humans to ensure workplace safety. However, emerging industrial tech such as recent advancements in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and safety protocols have paved the way for a new era of collaboration between humans and robots. Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside humans in shared workspaces, enabling a seamless and safe coexistence. They are equipped with advanced sensors, vision systems, and safety features, which enable them to adapt to the presence of human workers. This opens new possibilities for flexible and efficient manufacturing processes.
There are many advantages to deploying and using HRC. First and foremost, cobots enhance productivity by automating repetitive and strenuous tasks. Second, this allows human workers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their work. Hence, the HRC collaborative approach improves overall efficiency and contributes to a more agile and adaptable production environment.
Autonomous Delivery Robots
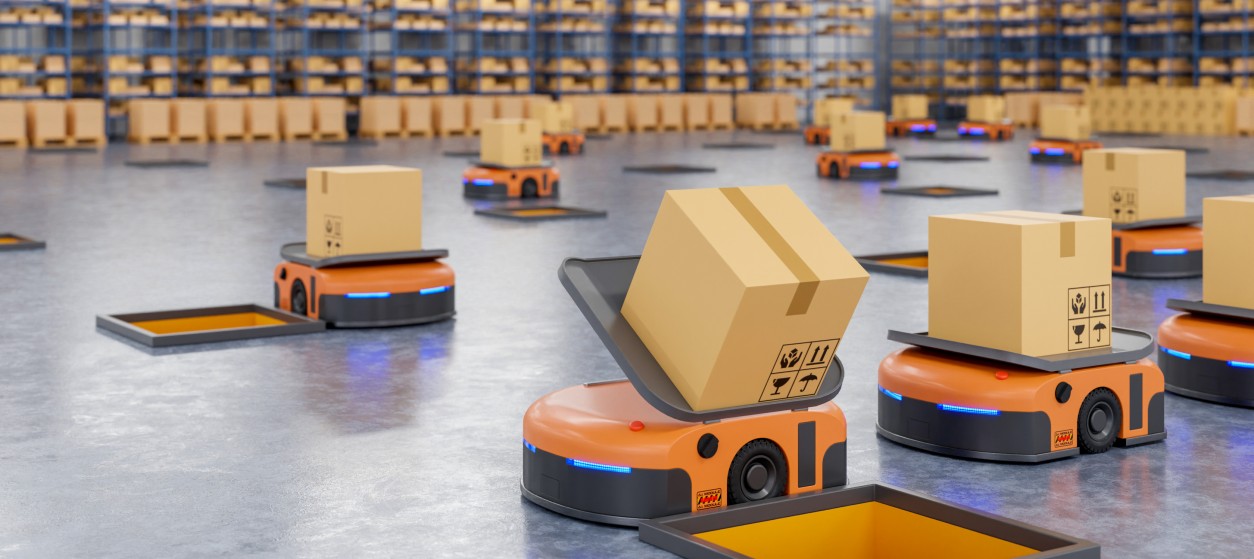
Beyond the limits of traditional industrial settings, autonomous delivery robots are nowadays emerging as an automation systems trend and a game-changer in logistics and supply chain management. These robots are designed to navigate through complex environments in order to deliver goods and packages autonomously. Based on the integration of AI, computer vision, and sensor technologies they can avoid obstacles, adapt to changing surroundings, and safely interact with pedestrians. Autonomous delivery robots have found applications in various sectors, including e-commerce, retail, and healthcare. They offer a cost-effective and efficient solution for last-mile delivery. This solution reduces reliance on traditional delivery methods and contributes to the optimization of logistics operations.
Autonomous robots are also used in urban environments to navigate sidewalks and public spaces in order to provide a sustainable and congestion-reducing alternative to traditional delivery vehicles. The rise of autonomous delivery robots showcases how robotics is expanding beyond manufacturing floors, transforming the way goods are transported and delivered in the modern world. Automation delivery robots are therefore, without doubt, one of the cutting-edge automation trends and one of the most popular industrial automation trends.
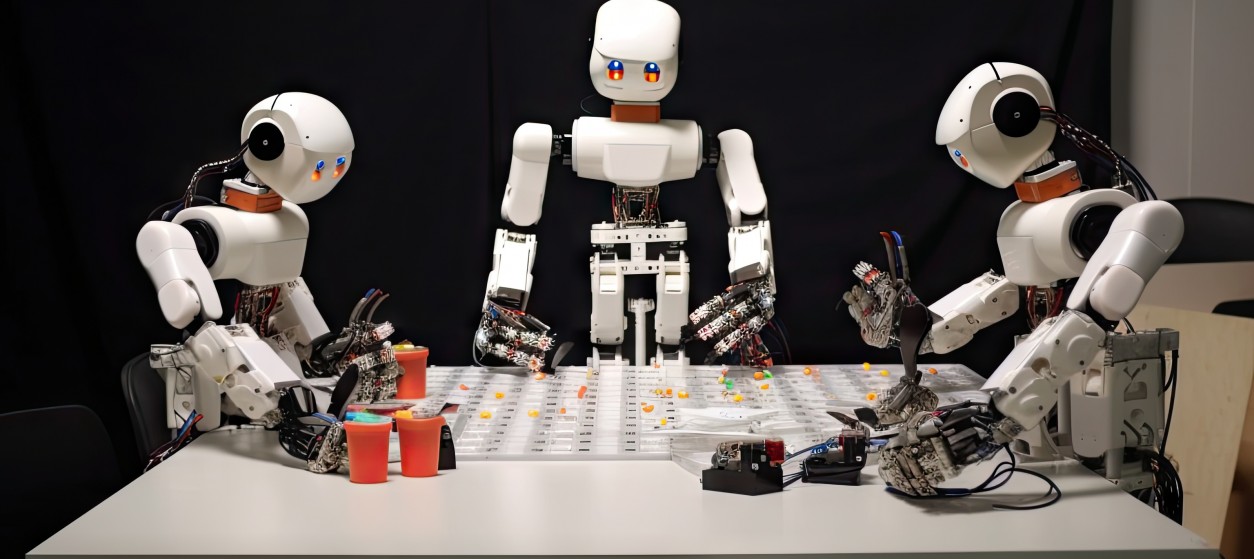
Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are designed to resemble and mimic human capabilities. This represents another fascinating trend in industrial robotics. These robots are equipped with advanced sensors, articulated limbs, and sophisticated AI systems, enabling them to perform tasks that traditionally required human intervention. Humanoid robots find applications in diverse industries, from healthcare and customer service to education and entertainment. In manufacturing, they can take on complex tasks that demand dexterity and precision, such as assembly and quality control. Humanoid robots are also making strides in medical settings, assisting with surgeries, rehabilitation, and patient care.
The development of humanoid robots reflects the industry’s quest to create machines that can seamlessly integrate into human-centric environments. In the future humanoid robots are likely to play an increasingly integral role in various industries, pushing the boundaries of what is achievable through automation.
Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS)
The Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) model is revolutionizing the way businesses approach robotics adoption. Instead of investing in expensive robotic hardware upfront, RaaS offers a subscription-based model where companies can lease robotic systems and pay for services on a usage basis. This approach lowers the barrier to entry for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), allowing them to leverage advanced robotic technologies without the need for substantial upfront capital investment. RaaS providers handle maintenance, updates, and support, enabling businesses to focus on their core operations.
RaaS models are gaining popularity in various industries, from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and agriculture. This trend democratizes access to cutting-edge robotics, making it more accessible to a broader range of businesses and accelerating the adoption of automation in diverse sectors.
Cloud Robotics
Cloud robotics is a robotics-related trend that leverages the power of cloud computing to enhance the capabilities of robots. This approach involves offloading computation, storage, and data processing to cloud servers, allowing robots to access vast amounts of data and computing resources in real-time. It is also an enabler of the above-presented RaaS business models.
Cloud robotics enables robots to learn from shared experiences, access up-to-date information, and collaborate with other robots through a centralized cloud infrastructure. This trend enhances the adaptability and intelligence of robots, making them more capable of handling complex tasks and dynamic environments. In industrial settings, cloud robotics facilitate remote monitoring, maintenance, and software updates, reducing downtime and improving overall system efficiency. The ability to centralize data and computation also contributes to the development of more intelligent and interconnected robotic systems.
Overall, the above-listed recent innovations in robotics are indicative of a dynamic and rapidly evolving field. Human-robot collaboration is redefining how robots and humans work together on the manufacturing floor, while autonomous delivery robots are transforming logistics and supply chain operations. Humanoid robots bring a touch of anthropomorphism to industrial tasks, while the Robot-as-a-Service model and cloud robotics are democratizing access to advanced robotic technologies and next-gen robotic solutions.
We predict that as technology advances (e.g., based on robotic technology advances and robotic manufacturing advances) these trends will continue to evolve giving rise to exciting automation technology updates. It is highly likely that the industrial robotics landscape is poised for further advanced robotics innovations and that it will create new possibilities for automation and efficiency across diverse industries. Industrial enterprises had better embrace these technological advancements and robotics technology updates, as they both enhance productivity and drive the next phase of industrial evolution towards increased intelligence and collaboration. This is in-line with the Industry 5.0 vision, which foresees that humans and robots will collaborate seamlessly to achieve new heights of efficiency and innovation.










Thanks for sharing this useful blog information.